You walk around your neighborhood and notice construction happening everywhere. New houses being built, old buildings being renovated, and establishments getting a fresh coat of paint. It makes you wonder, what exactly qualifies as a building improvement? Are there specific criteria that determine whether a project is considered an improvement or just regular maintenance? In this article, we will explore the various factors that classify a project as a building improvement, shedding light on the intricacies of this often misunderstood term.

This image is property of d2vlcm61l7u1fs.cloudfront.net.
Definition of Building Improvement
Understanding what is classified as a building improvement is crucial for anyone involved in real estate, construction, or property ownership. Building improvements refer to any modifications or enhancements made to a building structure that enhance its functionality, aesthetics, or overall value. These improvements can range from minor renovations to major structural changes and can be done to residential, commercial, or industrial buildings.
Importance of Understanding Building Improvements
Having a clear understanding of building improvements is essential for several reasons. First, it allows property owners to make informed decisions about potential upgrades or renovations to their buildings. By knowing what qualifies as a building improvement, they can prioritize specific areas to focus on and allocate their resources effectively.
Second, understanding building improvements is vital for contractors and construction professionals. It helps them accurately assess the scope and complexity of the project, plan the necessary resources, and provide accurate cost estimates to their clients.
Lastly, building improvements play a significant role in determining the value of a property. A well-maintained and upgraded building will have a higher market value, attracting potential buyers or tenants and ensuring a favorable return on investment.
This image is property of images.squarespace-cdn.com.
Different Types of Building Improvements
Building improvements can be categorized into several types, depending on the specific area or aspect being modified. These include structural improvements, exterior improvements, interior improvements, and accessory improvements. Let’s delve into each category in more detail.
Structural Improvements
Structural improvements involve modifications to the building’s foundation, roof, walls, or major systems. Here are some examples:
Foundation Repairs
Foundation repairs address any structural issues such as cracks, settling, or water damage. These repairs are essential to maintain the stability and safety of the building.
Roof Replacement
Roof replacement is necessary when the existing roof is deteriorating or damaged beyond repair. A new roof not only enhances the appearance of the building but also ensures protection against leaks and other weather-related issues.
Wall Reinforcement
Wall reinforcement involves strengthening the walls to improve their load-bearing capacity. This may include adding additional support beams or installing steel reinforcements to ensure the building’s structural integrity.
Addition of Elevators or Staircases
Adding elevators or staircases to a building can greatly enhance accessibility and convenience, especially in multi-story structures. This is particularly important for commercial buildings or those with accessibility requirements.
Installation of HVAC Systems
Installing HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems helps regulate the temperature, improve indoor air quality, and ensure energy efficiency. This is crucial in both residential and commercial buildings to provide comfort to occupants.
This image is property of media.wallstreetprep.com.
Exterior Improvements
Exterior improvements focus on enhancing the building’s facade, landscaping, and outdoor areas. Some examples include:
Installation of Windows or Doors
Upgrading windows and doors not only improves the aesthetics of the building but also enhances energy efficiency and security. Newer windows and doors can prevent drafts, reduce noise, and provide better insulation.
Upgrading Façade or Cladding
Upgrading the building’s facade or cladding can completely transform its appearance. This improvement can include replacing outdated materials, applying a fresh coat of paint, or even installing new siding to modernize the building’s exterior.
Construction of Balconies or Decks
Adding balconies or decks to a building increases its usable outdoor space, providing occupants with an area to relax or entertain. These additions can significantly enhance the building’s appeal and market value.
Landscaping and Hardscaping
Improving the landscaping and hardscaping of a building involves planting trees, flowers, or shrubs, creating pathways, installing outdoor lighting, and adding features like water fountains or seating areas. These enhancements not only improve the aesthetics but also contribute to a pleasant environment for occupants.
Interior Improvements
Interior improvements focus on enhancing the appearance, functionality, and comfort of the building’s interior spaces. Some examples include:
Renovations to Flooring, Walls, or Ceilings
Renovations to flooring, walls, or ceilings can transform the look and feel of a building’s interior. This may involve replacing old carpets with hardwood floors, repainting walls, or installing decorative ceiling tiles.
Upgrades to Plumbing or Electrical Systems
Upgrading plumbing or electrical systems is essential for both safety and functionality. This improvement may include replacing outdated pipes or wiring, installing energy-efficient fixtures, or incorporating smart home technology.
Addition or Modification of Room Layouts
Modifying the room layouts allows for better space utilization and customization according to the occupants’ needs. This may involve removing or adding walls, creating open-concept spaces, or redesigning the flow of rooms.
Installation of Built-in Fixtures or Appliances
Installing built-in fixtures or appliances, such as cabinets, shelving, or built-in kitchen appliances, optimizes storage space and improves overall functionality. These additions can enhance the convenience and aesthetics of the building’s interior.

This image is property of www.investopedia.com.
Accessory Improvements
Accessory improvements refer to enhancements made to the building’s exterior structures or amenities. Some examples include:
Construction of Detached Garages or Sheds
Constructing detached garages or sheds provides additional storage, parking, or workspace. These structures can be valuable additions for both residential and commercial properties.
Installation of Fences or Gates
Fences or gates enhance security, privacy, and aesthetics for a property. They help define boundaries and control access, giving occupants peace of mind.
Building of Pools or Spas
Installing pools or spas can create a luxurious and relaxing atmosphere, particularly in residential buildings. These additions can increase the property’s appeal and value.
Creation of Outdoor Living Spaces
Creating outdoor living spaces, such as patios, decks, or outdoor kitchens, expands the usable area of the building and provides opportunities for relaxation and entertainment. These spaces can significantly improve the overall quality of life for occupants.
Permits and Regulations
When undertaking building improvements, it is essential to comply with necessary permits and regulations to avoid legal issues and ensure safety. Understanding the following aspects is vital:
Importance of Obtaining Permits
Obtaining permits is crucial to ensure that the planned improvements meet local building codes, zoning regulations, and safety standards. Failure to obtain permits can result in fines, delays, or even being required to undo the improvements.
Compliance with Local Building Codes
Local building codes dictate the minimum standards for construction, plumbing, electrical work, and other aspects of building improvements. Complying with these codes is essential to ensure the safety and structural integrity of the building.
Understanding Zoning Regulations
Zoning regulations govern how land and buildings can be used within a specific area. It is crucial to understand these regulations to ensure that the proposed improvements are permitted. These regulations may include restrictions on building height, setbacks, or land usage.

This image is property of www.universalcpareview.com.
Costs and Financing
Building improvements involve significant costs, and understanding the financial implications is crucial. Consider the following aspects:
Determining the Financial Impact
Assess the financial impact of the proposed building improvements by estimating the costs involved, including materials, labor, permits, and professional fees. This helps determine if the improvements are feasible within the available budget.
Budgeting for Building Improvements
Creating a budget for building improvements helps prioritize different aspects and allocate resources accordingly. It ensures that the project remains within financial constraints and prevents overspending.
Options for Financing
There are various options available to finance building improvements, such as personal savings, loans, or lines of credit. It is essential to explore different financing options and choose the one that best suits the individual’s or organization’s financial situation.
Tax Implications
Building improvements can have tax implications, which should be considered before proceeding. Some key points to keep in mind include:
Property Tax Assessment and Increases
Significant building improvements can lead to an increase in the property’s assessed value, resulting in higher property taxes. It is important to consider these potential increases when evaluating the financial feasibility of the improvements.
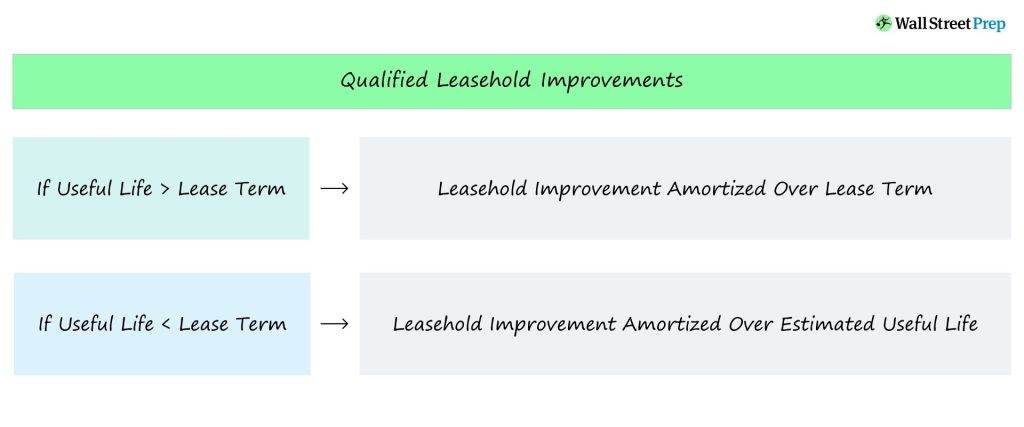
Depreciation and Capitalization
Certain building improvements may qualify for depreciation or capitalization, allowing the costs to be spread out over time for tax purposes. Consult with a tax professional to understand the specific rules and requirements for depreciation or capitalizing improvements.
Tax Deductions and Incentives
In some cases, building improvements may be eligible for tax deductions or incentives. These can include deductions for energy-efficient upgrades or incentives for historic preservation. Familiarize yourself with any available tax incentives to maximize potential savings.
Considerations for Building Improvements
Before embarking on building improvements, consider the following factors:
Maintenance and Longevity
Ensure that the improvements are designed and constructed to minimize future maintenance requirements and maximize their lifespan. This includes using durable materials, implementing proper maintenance practices, and considering the long-term costs of upkeep.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Integrating energy-efficient features and sustainable practices into building improvements can reduce operational costs and environmental impact. Consider options such as energy-efficient windows, insulation, renewable energy sources, and water-saving fixtures.
Aesthetics and Market Value
Building improvements should enhance the aesthetics of the property and align with current design trends. Consider the potential impact on market value and the preferences of potential buyers or tenants in the future.
Functional and Operational Enhancements
Focus on improving the functionality and operational efficiency of the building. Consider the needs of the occupants, accessibility requirements, technological advancements, and any improvements that can streamline processes or enhance productivity.
Conclusion
Understanding building improvements is essential for property owners, contractors, and construction professionals. With the knowledge of different types of improvements, permitting regulations, costs, financing options, tax implications, and other considerations, individuals can make informed decisions and ensure successful building improvement projects. By enhancing the structure, interior, exterior, and accessories of a building, it becomes more functional, aesthetically pleasing, and valuable. Whether it’s a small renovation or a major structural change, building improvements have the potential to significantly enhance the overall quality and appeal of any property.